The World Viewed by Cetaceans
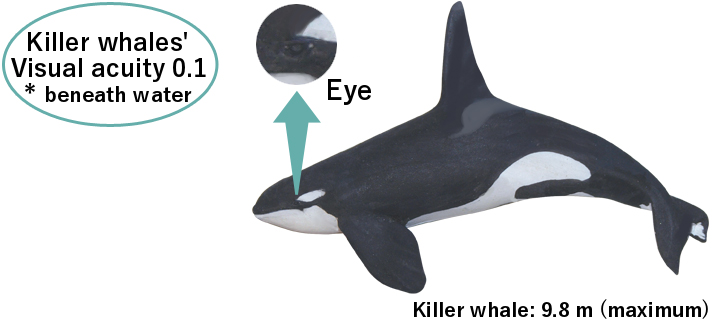
Cetaceans have surprisingly small eyes compared to their size.
It is thought to reduce water resistance and to provide better vision by using a pinhole-camera like structure.
Cetaceans can only see across very short distances, less than 1 meter underwater, while they can easily see across longer distances of 2.5 km or more above water.
The World that Cetaceans See
The Worlds of Visual Acuity 1.0 and 0.1

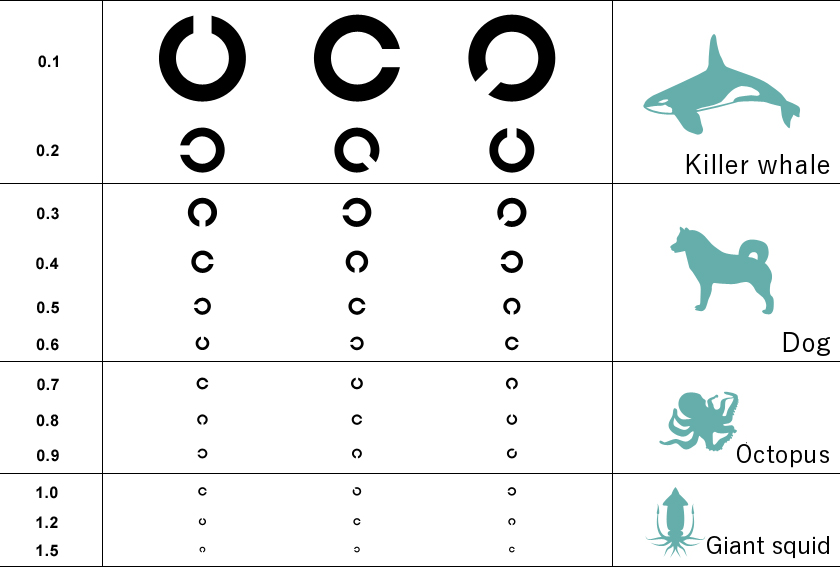
Beneath the water, the visual acuity of killer sharks is around 0.1, which is supposedly as blurry as the picture above.
The Visual Acuity of Various Animals Animals have different visual acuity depending on their environment and the way they live.
The World Heard by Cetaceans
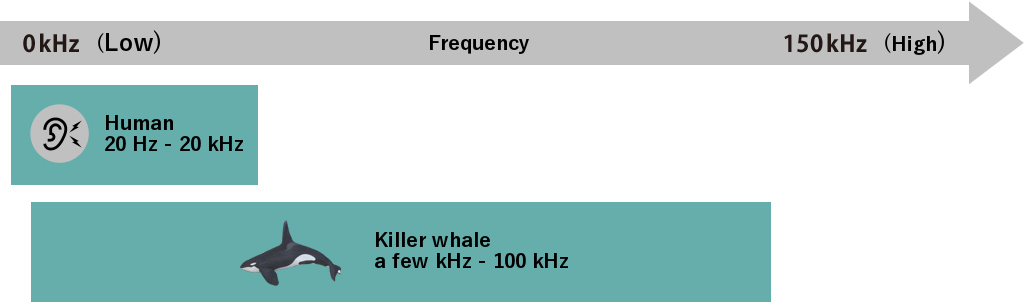
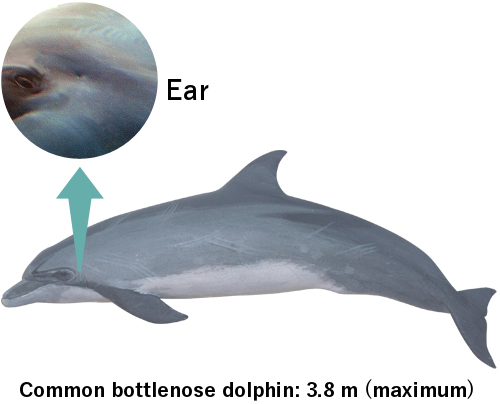
Humans can hear sound ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, while some cetaceans can hear lower or higher sounds than we can. Dolphins can hear from 10 or 20 kHz to as high as 150 kHz, and killer whales can hear a wide range of sound even lower than 100 kHz. Their acute sense of sound enables them to communicate with each other and find prey underwater with limited vision.
The Sounds that We Hear and the Sounds that Cetaceans Hear
Killer whales are among the largest species in the Delphinidae with long cochlea, a spiral-shaped cavity, that is best suit to decipher lower frequency sound.
Ordinary Delphinidae can decipher 11kHz to 18kHz while killer whales can hear lower kHz to 100kHz. Higher hearing ability enable them to communicate each other and capture their preys.